1H: 100% spin = 1/2
4 × spin = 1/2 neighbours

5 peaks (1:4:6:4:1)
19F: 100% spin = 1/2
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour

2 peaks (1:1)
117Sn: 8% spin = 1/2
119Sn: 9% spin = 1/2
other Sn: 83% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (9%, largest coupling)
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (8%, smallest coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbour (83%, no coupling)

5 peaks (9:8:166:8:9)
14N: 100% spin = 1
1 × spin = 1 neighbour
2nI + 1 = 2(1)(1) + 1 = 3
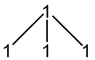
3 peaks (1:1:1)
13C: 1% spin = 1/2
other C: 99% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (1%, only coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbour (99%, no coupling)
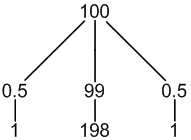
3 peaks (1:198:1)
77Se: 8% spin = 1/2
other Se: 92% spin = 0
2 × spin = 1/2 neighbours (8%, only coupling)
2 × spin = 0 neighbours (92%, no coupling)

5 peaks (1:46:531:46:1)
27Al: 100% spin = 5/2
1 × spin = 5/2 neighbour
2nI + 1 = 2(1)(5/2) + 1 = 6
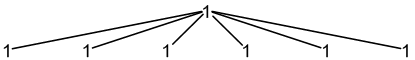
6 peaks (1:1:1:1:1:1)
2H: 100% spin = 1
2 × spin = 1 neighbours
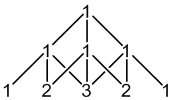
5 peaks (1:2:3:2:1)
19F: 100% spin = 1/2
6 × spin = 1/2 neighbours
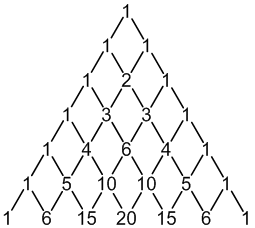
7 peaks (1:6:15:20:15:6:1)
203Tl: 30% spin = 1/2
205Tl: 70% spin = 1/2
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (70%, largest coupling)
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (30%, smallest coupling)

4 peaks (7:3:3:7)
1H: 100% spin = 1/2
CH2: 3 × spin = 1/2 neighbours
CH3: 2 × spin = 1/2 neighbours
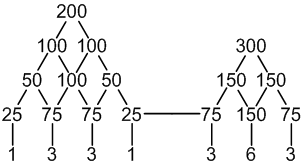
7 peaks (1:3:3:1 : 3:6:3)
69Ga: 60% spin = 3/2
71Ga: 40% spin = 3/2
1 × spin = 3/2 neighbour (60%, smaller coupling)
1 × spin = 3/2 neighbour (60%, larger coupling)

8 peaks (2:3:2:3:3:2:3:2)
195Pt: 33% spin = 1/2
other Pt: 67% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (33%, only coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbours (67%, no coupling)
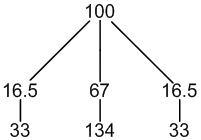
3 peaks (33:134:33)
2H: 100% spin = 1
4 × spin = 1 neighbours (1%, only coupling)

9 peaks (1:4:10:16:19:16:10:4:1)
107Ag: 52% spin = 1/2
109Ag: 48% spin = 1/2
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (48%, largest coupling)
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (52%, smallest coupling)

4 peaks (12:13:13:12)
183W: 14% spin = 1/2
other W: 86% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (14%, only coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbours (86%, no coupling)
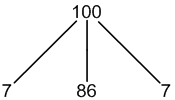
3 peaks (7:86:7)
31P: 100% spin = 1/2
2 × equivalent P: 1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour
Unique P: 2 × spin = 1/2 neighbours
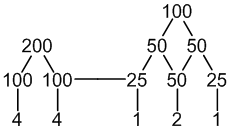
7 peaks (4:4 : 1:2:1)
63Cu: 69% spin = 3/2
65Cu: 31% spin = 3/2
1 × spin = 3/2 neighbour (31%, largest coupling)
1 × spin = 3/2 neighbour (69%, smallest coupling)
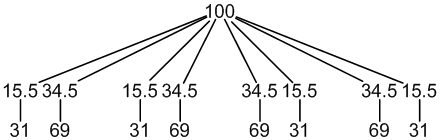
8 peaks (31:69:31:69:69:31:69:31)
10B: 20% spin = 3
11B: 80% spin = 3/2
1 × spin = 3 neighbour (20%, integer coupling values)
1 × spin = 3/2 neighbour (80%, half-integer coupling values)

11 peaks (1:1:7:1:7:1:7:1:7:1:1)
31P: 100% spin = 1/2
6 × spin = 1/2 neighbours

7 peaks (1:6:15:20:15:6:1)
77Se: 8% spin = 1/2
other Se: 92% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (8%, only coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbour (92%, no coupling)
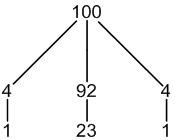
3 peaks (1:23:1)
1H: 100% spin = 1/2
1 × CH: 6 × spin = 1/2 neighbours
2 × CH3: 1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour
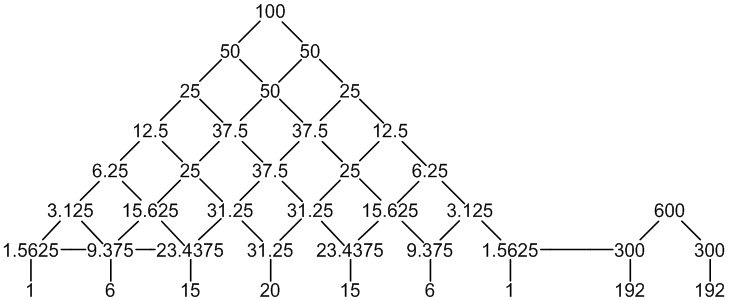
9 peaks (1:6:15:20:15:6:1 : 192:192)
29Si: 5% spin = 1/2
other Si: 95% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (5%, only coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbour (95%, no coupling)
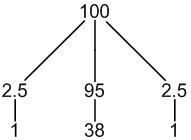
3 peaks (1:38:1)
195Pt: 33% spin = 1/2
other Pt: 67% spin = 0
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (33%, only coupling)
1 × spin = 0 neighbours (67%, no coupling)
19F: 100% spin = 1/2
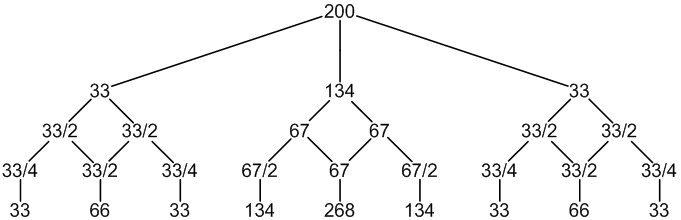
9 peaks (33:66:33 : 134:268:134 : 33:66:33)
2H: 100% spin = 1
3 × spin = 1 neighbours
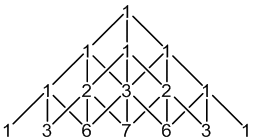
7 peaks (1:3:6:7:6:3:1)
103Rh: 100% spin = 1/2
31P: 100% spin = 1/2
unique P:
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (Rh, largest coupling), 2 × spin = 1/2 neighbours (P, smallest coupling)
2 × equivalent P:
1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (Rh, largest coupling), 1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour (P, smallest coupling)
19F: 100% spin = 1/2
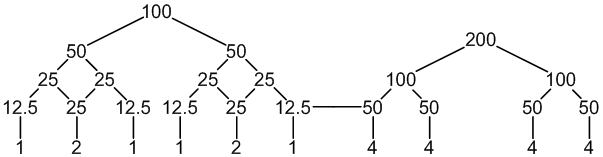
10 peaks (1:2:1:1:2:1 : 4:4:4:4)
1H: 100% spin = 1/2
CH: 3 × spin = 1/2 neighbours
CH3: 1 × spin = 1/2 neighbour

6 peaks (1:3:3:1 : 12:12)
29Si: 5% spin = 1/2
other Si: 95% spin = 0
2 × spin = 1/2 neighbours (5%, only coupling)
2 × spin = 0 neighbours (95%, no coupling)

5 peaks (1:76:1446:76:1)